Compounds

Defined: A Compound is a substance formed when two or more different chemical elements are chemically bonded together.
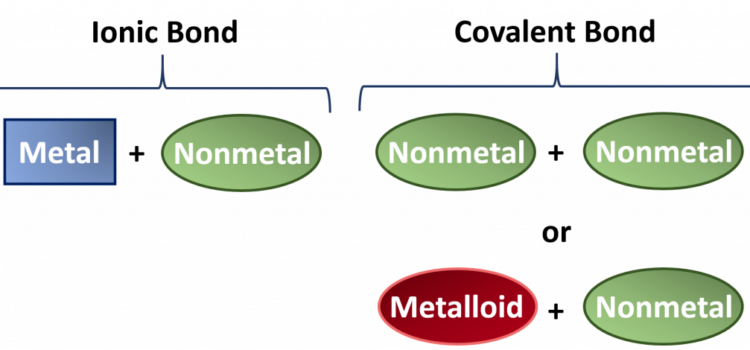
- Define: ionic compound, molecular compound, covalent compound, ionic bond, covalent bond, molecule, electrostatic force
- Understand the differences and similarities between a compound and a molecule
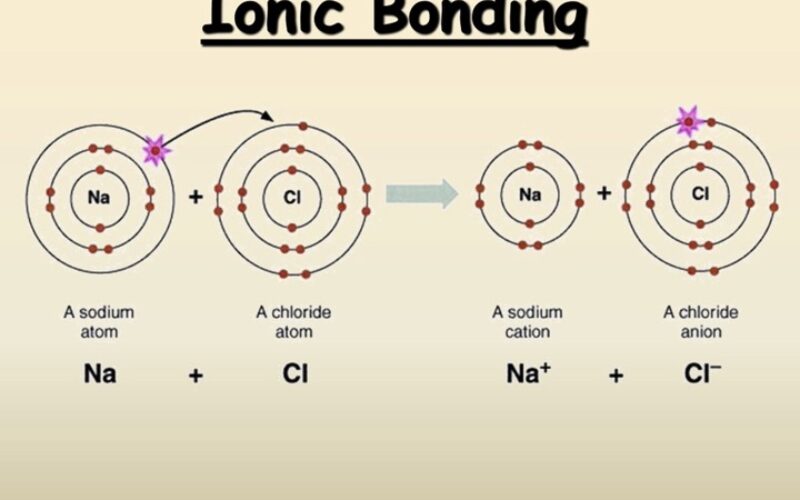
- Describe how an ion is formed and understand the difference between cations and anions
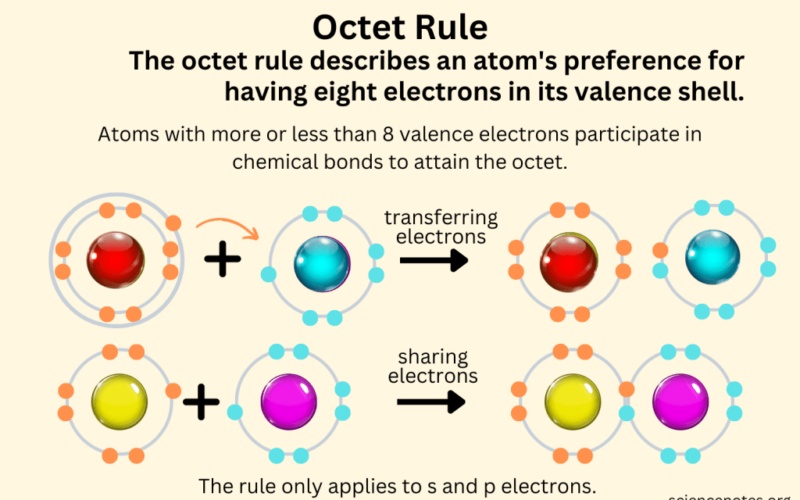
- Use the octet rule and electron configurations to determine if an atom will gain or lose electrons forming anions or cations.
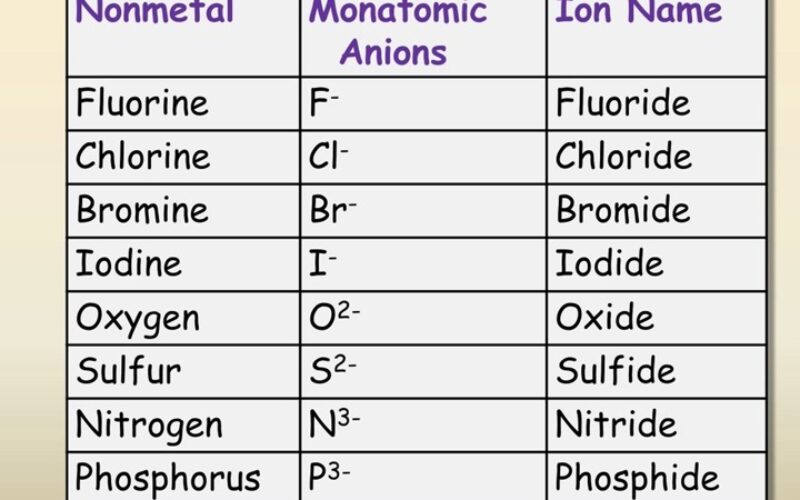
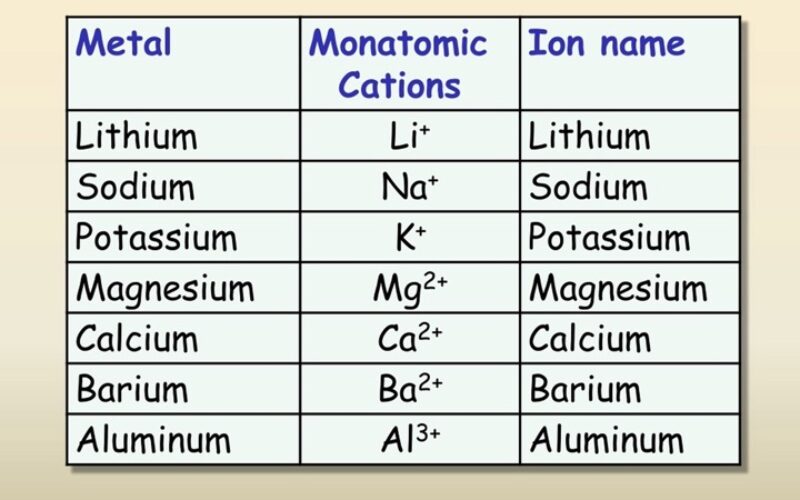
- Become familiar with the charge of some common ions.
- Use the periodic table to predict ion charge.
- Name some common ions
- Develop an understanding of the 3-dimmensional nature of electrostatic attractions in ionic compounds
- Name and write formulas of some common ionic compounds
- Name and write formulas of some covalent compounds
- Describe the basic physical properties of ionic compounds, covalent compounds, and how they differ.
- Develop an understanding of how the octet rule influences covalent bonds.
- Understand how the positions of atoms in the periodic table is related to their behavior in compounds.
- Understand the formation of multiple covalent bonds between two atoms
- Use electronegativity to determine whether a covalent bond is polar
- Understand the role of polarity in properties of molecules and solutions

Ions
Ions are electrically charged particles formed when atoms gain or lose one or more electrons.
- Cations: When an atom loses one or more electrons, it becomes positively charged because it has more protons than electrons. These positively charged ions are called cations.
- Anions: When an atom gains one or more electrons, it becomes negatively charged because it has more electrons than protons. These negatively charged ions are called anions.
Shells
The electron shells of an atom are populated from the inside out, with electrons filling up the low-energy shells closer to the nucleus before they move into the higher-energy shells further out.
The Periodic Table
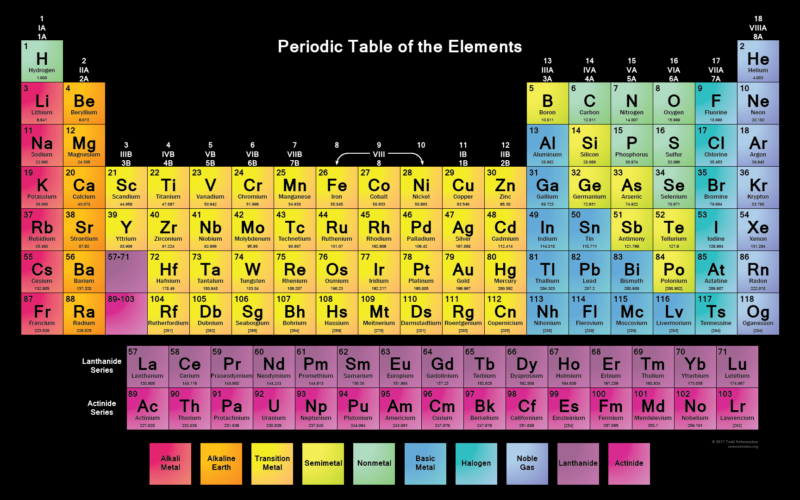
As you move along each row (or period), there are repeating patterns in the chemical and physical properties of the elements in each one. For example, you’ll find metals on the left-hand side and non-metals on the right.