What is Chemistry?
Chemistry is the study of the composition of matter and the changes that
matter undergoes. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space.
Virtually everything around us is matter, including both living and
nonliving things.
Chemistry is the study of the
composition of matter and the
changes that matter undergoes.
Matter is anything that has mass
and takes up space. Virtually
everything around us is matter,
including both living and
nonliving things.

Key Terms
Macroscopic: refers to substances and objects that can be seen, touched, and measured directly.
Microscopic: refers to the small particles that make up all matter.
Matter: is defined as anything that has mass and volume.
Mass: is a measure of the amount of matter in a substance or an object.
Volume: is a measure of the amount of space that a substance or an object takes up.
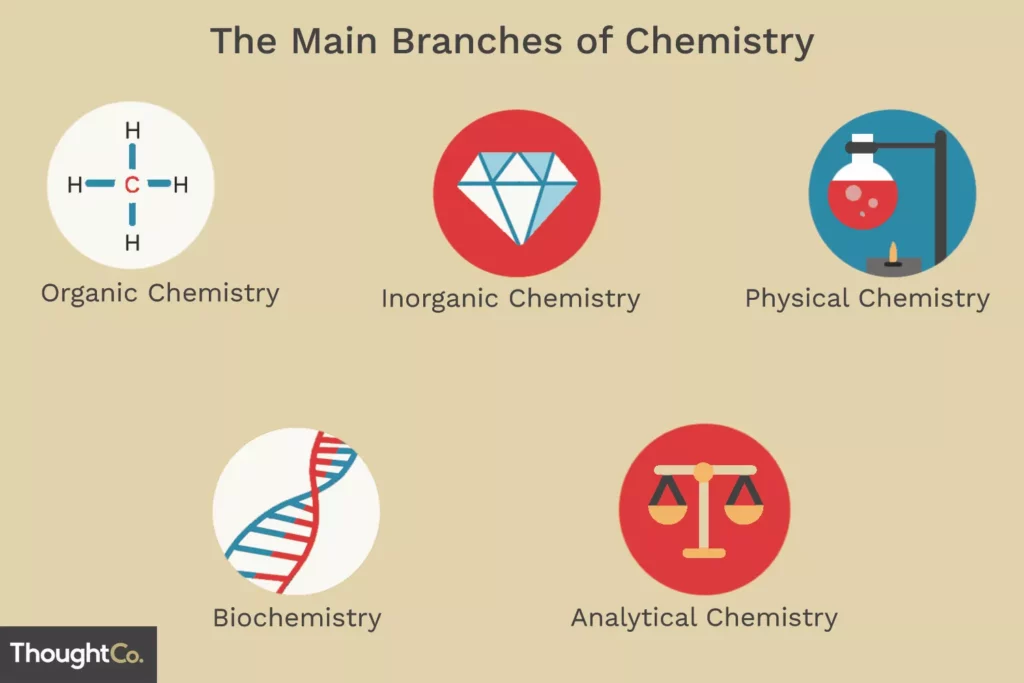
Areas of Chemistry
The study of modern chemistry has many branches, but can generally be
broken down into five main disciplines, or areas of study.
The study of modern chemistry
has many branches, but can
generally be broken down into
five main disciplines, or areas
of study.
Physical chemistry is the study of macroscopic properties, atomic properties, and phenomena in chemical systems.
Organic chemistry is the study of chemicals containing carbon. Most chemicals found in every living organism are based on carbon.
Inorganic chemistry is the study of chemicals that do not, in general, contain carbon. Inorganic chemicals are commonly found in rocks and minerals.
Analytical chemistry is the study of the composition of matter. It focuses on separating, identifying, and quantifying chemicals in samples of matter.
Biochemistry is the study of chemical processes that occur in living things. Research may cover basic cellular processes up to understanding disease states.
States of Matter
Matter typically exists in one of three states: solid, liquid, or gas.
There is a fourth state of matter called plasma, which rarely exists on
earth.
Matter typically exists in one
of three states: solid, liquid,
or gas. There is a fourth state
of matter called plasma, which
rarely exists on earth.
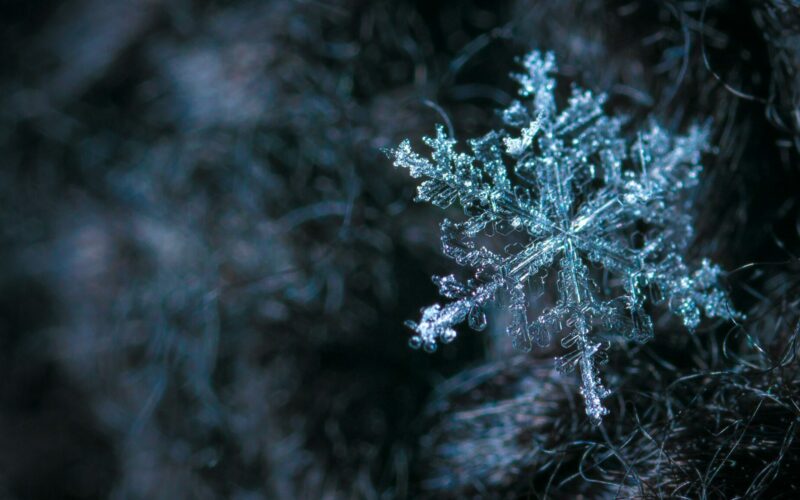
Solid
Solids are defined by the following characteristics:
- Definite shape (rigid).
- Definite volume.
- Particles vibrate around fixed axes.


Liquid
Liquids have the following characteristics:
- No definite shape (takes the shape of its container).
- Has definite volume.
- Particles are free to move over each other, but are still attracted to each other.
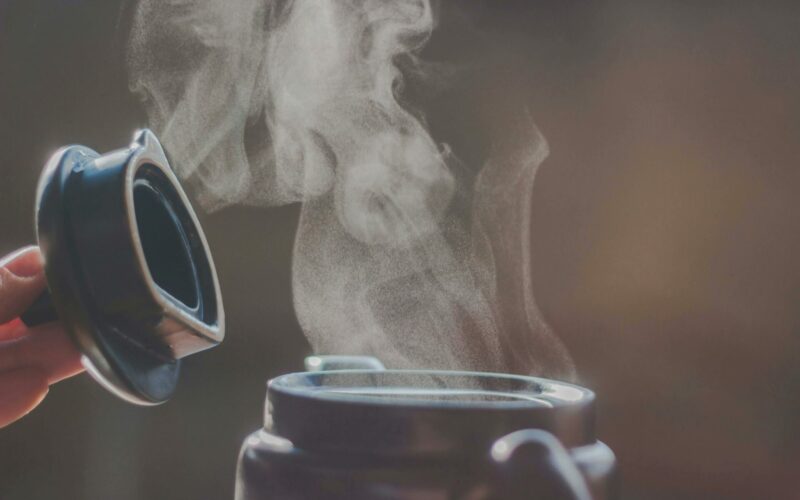
Gas
Gases have the following characteristics:
- No definite shape (takes the shape of its container).
- No definite volume.
- Particles move in random motion with little or no attraction to each other.
- Highly compressible.
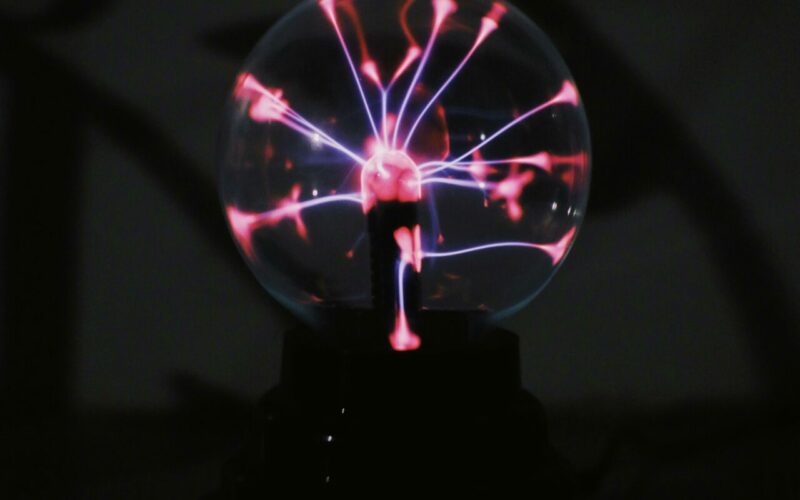


Plasma
Plasma are defined by the following characteristics:
- particles are charged ions and free electrons
- no definite shape
- no definite volume
- conducts electricity
- responds to magnetic field